As the Asset Management Council of Australia emphasizes, effective asset management provides organizations with insights across four critical domains: physical, information, financial, and intellectual assets. When implemented successfully, it enhances decision-making, strengthens operational resilience, and delivers long-term value. This capability serves as a key differentiator between agile, modern factories and slower, fragmented legacy operations.
The next frontier of asset management explores the shift from human-dependent monitoring to autonomous systems—where assets effectively manage themselves.
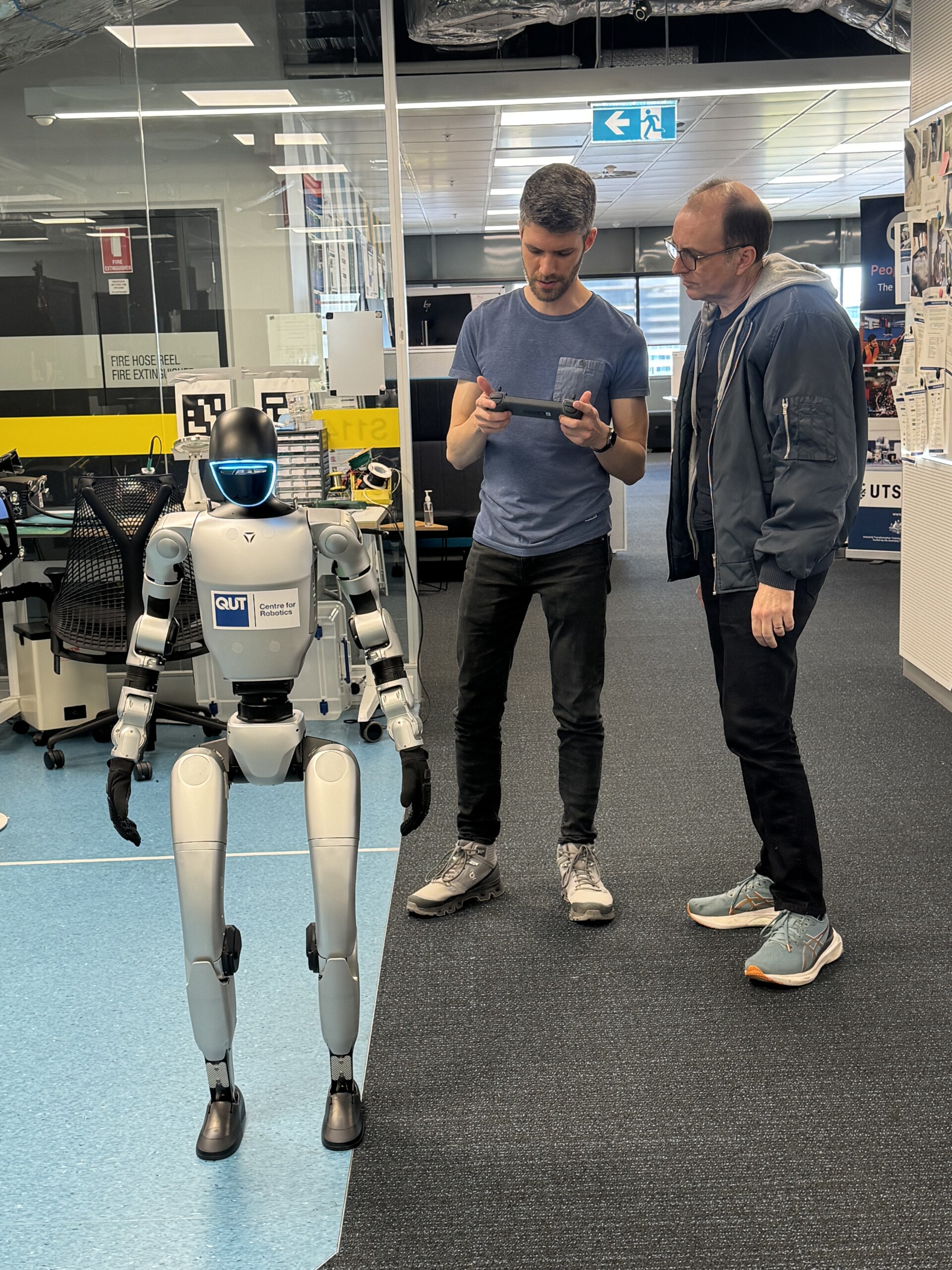
Under the Australian Cobotics Centre’s (ACC) Quality Assurance and Compliance program, researchers at the UTS:Robotics Institute are advancing this concept through the deployment of Boston Dynamics’ robotic platform, Spot. In this implementation, Spot autonomously navigates industrial environments, constructs a digital map, captures detailed imagery of equipment such as pipes, coils, and panels, and performs inspection tasks without human supervision.
Collaborative robots, or cobots, play a critical role in this evolving landscape. Designed to complement rather than replace human workers, cobots enhance manufacturing resilience by integrating human judgment with machine-level consistency and precision. Studies by [1] and [2] highlight the synergy of cobots and human teams in improving factory adaptability.
In this approach, robots such as Spot undertake detailed inspection routines, while humans execute follow-up tasks—tightening components, initiating repairs, or notifying human operators through shared digital interfaces. A supporting fleet management system, as outlined by [3], enables real-time tracking of cobot performance, usage, and maintenance status, effectively treating each cobot as a digital asset within the broader ecosystem.
In field trials, Spot demonstrated 90 minutes of continuous operation without a battery swap, covering 7.5 kilometers of factory floor—equivalent to 75,000 m². This capacity enables a single robot to replace multiple manual inspection rounds per shift in a typical Australian SME manufacturing facility.
A key innovation in the system is an integrated asset-management dashboard that connects directly to the SPOT’s API. By aggregating live telemetry, annotated inspection imagery, and equipment metadata, the dashboard eliminates the need for manual data entry. During initial deployments, Spot completed multi-kilometre inspection loops and uploaded over 6,000 annotated images per shift, delivering a comprehensive, timestamped view of equipment health. The dashboard’s real-time capabilities position it as a dynamic decision-support tool, advancing the transition from reactive maintenance to proactive, autonomous operations.
This trial represents a foundational step toward scaling autonomous survey robotics across industry. The integration of AI-driven perception, robotic mobility, and collaborative tasking is redefining the asset management paradigm.
The convergence of autonomous robotics, AI-powered vision systems, and collaborative machines signals a fundamental transformation in industrial asset management. Tasks once characterized by manual oversight are becoming intelligent, continuous processes. Initiatives such as those under the Australian Cobotics Centre offer a forward-looking model where factory systems are capable of sensing, interpreting, and responding with minimal human input—enabling safer, smarter, and more resilient operations across the manufacturing sector.
Citation: https://www.nbnco.com.au/blog/the-nbn-project/the-power-of-robotics-to-lift-digital-capability
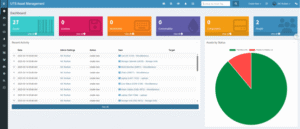
Text – Asset Dashboard
[1] J. Pizoń, M. Cioch, Ł. Kański, and E. Sánchez García, “Cobots Implementation in the Era of Industry 5.0 Using Modern Business and Management Solutions,” Adv. Sci. Technol. Res. J., vol. 16, no. 6, pp. 166–178, Dec. 2022, doi: 10.12913/22998624/156222.
[2] A. R. Sadik and B. Urban, “An Ontology-Based Approach to Enable Knowledge Representation and Reasoning in Worker–Cobot Agile Manufacturing,” Future Internet, vol. 9, no. 4, Art. no. 4, Dec. 2017, doi: 10.3390/fi9040090.
[3] B. I. Ismail, M. F. Khalid, R. Kandan, H. Ahmad, M. N. Mohd Mydin, and O. Hong Hoe, “Cobot Fleet Management System Using Cloud and Edge Computing,” in 2020 IEEE 7th International Conference on Engineering Technologies and Applied Sciences (ICETAS), Dec. 2020, pp. 1–5. doi: 10.1109/ICETAS51660.2020.9484266.