POSTED: 23 Oct, 2023
Written by Postdoctoral Research Fellow, Dr. Anushani Bibile and Research Program Co-Lead, Dr. Michelle Dunn, both from SUT
A collaborative robot (or cobot) is designed to work side-by-side with people and can support applications from welding, pick and place, injection moulding, CNC, packaging, palletising, assembly, machine tending and materials handling. The integration of cobots enables the delegation of many human-based skill activities, with cobots able to undertake a range of repetitious tasks, whilst offering high flexibility and increased productivity.
A collaborative robot arm is compact, occupying a smaller floorspace than a conventional robot and can offer great flexibility for ‘low-volume, high-mix’ production, or high specialisation environments.
It is easier to re-program and re-tool a cobot to undertake a range of actions, providing greater agility as well as reductions in cost of operation. As cobots are also designed to work safely side-by-side with human operators, reduced safety measures are required when compared with a conventional robot.
If you are thinking of integrating a cobot into your manufacturing process it is important to look at the quality assurance of your system. When implementing a conventional robot, you would ensure the quality assurance was satisfied during initial setup, but when you use a cobot, which can be reconfigured for different processes, you need to consider the quality assurance every time you make a change. Changes to the code by non-experts, will have to be checked and verified very closely and safety always needs to be considered. Therefore, quality assurance is critical for human-cobot systems in automated processes as it ensures that the products or services produced meet the required specifications and are safe for use.
Why are continuous quality assurance checks important for human-cobot systems?
- Productivity: Quality assurance measures can help optimise the performance of a human-cobot system, improve productivity and reducing waste. This can include monitoring and controlling the system to ensure that it is working efficiently and identifying areas where improvements can be made.
- Safety: Safety is a critical concern when it comes to human-cobot systems. A cobot does not need to be caged, therefore a malfunctioning or improperly programmed cobot can cause serious injury or damage to humans or equipment. Quality assurance measures help ensure that the cobot system is designed and programmed correctly, and that it is safe for use.
- Compliance: Quality assurance measures can help ensure that a human-cobot system meets regulatory and industry standards. This can include performing audits and inspections to ensure that the system is operating within the required parameters and that all safety regulations are being followed.
If proper quality assurance measures are not in place, there are potential risks associated with human-cobot systems. Some of these risks include:
- Malfunctioning: A cobot that is not properly programmed or maintained can malfunction, causing damage or injury to humans or equipment.
- Inaccuracy: A poorly calibrated or inaccurate cobot can produce defective products or services, leading to waste, customer dissatisfaction, and potentially legal liabilities.
- Cybersecurity: Human-cobot systems are susceptible to cyber threats, which can lead to system failures, data breaches, and other security issues. Quality assurance measures can help ensure that the system is secure and that appropriate cybersecurity protocols are in place.
Design of safety mechanisms must meet the corresponding industrial standards which are exemplified in the figure below. First, a cobot must meet the relevant safety requirements, laws and directives for general machinery such as the European Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC). Basic safety rules and regulations (known as Type A standards) must also be met. Specific applications of a cobot system must meet type B standards. Finally, the cobots as products must meet type C standards.
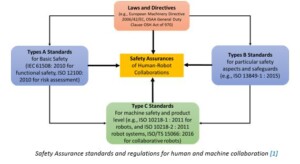
Safety Assurance standards and regulations for human and machine collaboration [1]
Finally, it is important to regularly review and update quality assurance protocols to keep pace with evolving technologies and changing workplace conditions. By remaining vigilant and proactive in preserving the quality assurance of cobots in automated processes, organisations can reap the benefits of cobot automation while minimising risks and maximising productivity.
[1]Bi, Z. M., et al. (2021). “Safety assurance mechanisms of collaborative robotic systems in manufacturing.” Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing 67.
[2] Vicentini, F. (2021). “Collaborative Robotics: A Survey.” Journal of Mechanical Design 143(4).
Recent News
ARTICLE: Solving manufacturing’s labour crunch: Why job quality and collaborative robots must go hand-in-hand
The Albanese Government’s Future Made in Australia agenda has committed $22.7 billion over the next decade to rebuild sovereign manufacturing capabi ...
Celebrating the Robotics & Advanced Manufacturing Centre at TAFE Queensland!
On 17th June 2025, our Centre was part of the official opening of the Robotics and Advanced Manufacturing Centre (RAMC) at TAFE Queensland Eagle Farm ...
Meet our E.P.I.C. Researcher, Sheila Sutjipto
Sheila Sutjipto is a Postdoctoral Research Fellow in the Biomimic Program where her research explores physical human–robot interaction (pHRI). She ...